Product Description
Cement equipment Gear Coupling Shaft Couplings Toothed Gear Coupling
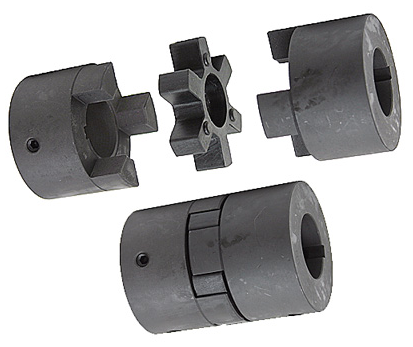
Product show
| Product Name | Densen customized GIICL gear motor shaft coupling,machine shaft coupling,flexible gear coupling |
| DN mm | 16-1040mm |
| Rated Torque | 0.4~4500 kN·m |
| Allowalbe Speed | 4000~460RPM |
| Material | 45# Steel or 42CrMo |
| Application | Widely used in metallurgy, mining, engineering and other fields. |
Why Choose Us
1. One stop service:
We have 5 own factories and 50+ sub-contractors located in different areas of China to offer you one-stop manufacturing and purchasing services to help you save time and reduce procurement cost.
2. Your eyes in China:
Our commitment to quality permeates from quoting, scheduling, production, inspection to deliver into your warehouse, our QC team will remark the errors if has on QC documents for your checking before delivery as your 3rd party.
3. Your R&Dconsultant:
With professional engineers team and 29 years manufacture experience ,we would help you work out problems during new parts’ development, optimize design and recommend the most cost-effective solution.
4. Your Emergency Solver:
With continued grown factories team and our QC teams located in different areas, if customers need to expedite the delivery, we would be able to adopt another factory to produce together immediately.
5. Quality Guaranty:
No matter how long time the products delivered, we are responsible for the quality. In case the products be rejected, we would replace them or return fund according to your demand without hesitation
FAQQ1. Are you a manufacturer or a trader?
Manufacture, we have 5 own foundries, 4 in ZheJiang Province, 1 in ZHangZhoug Province
Q2. Do you have MOQ request?
1 pcs per order is ok with us , unless material is seldom used.
Q3. If I only have a sample,without drawings, can you quote then manufacture for me?
Just send us the sample, we would have the sample simulated and measured by professional equipment then issue formal drawings for
you , at the same time, we could help you optimize the design according to your demand and related processes’ feasibility.
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1

Can Shaft Couplings Compensate for Angular, Parallel, and Axial Misalignments?
Yes, shaft couplings are designed to compensate for different types of misalignments between rotating shafts in mechanical power transmission systems. They can handle the following types of misalignments:
- Angular Misalignment: This occurs when the shafts are not parallel and have an angle between them. Flexible couplings, such as elastomeric, beam, or Oldham couplings, can accommodate angular misalignments by allowing slight angular movement between the shafts while transmitting torque.
- Parallel Misalignment: This happens when the shafts are not collinear, resulting in axial displacement. Flexible couplings with lateral flexibility, like elastomeric or bellows couplings, can handle parallel misalignment by allowing limited lateral movement between the shafts.
- Radial Misalignment: Radial misalignment occurs when the shafts have lateral displacement but remain parallel. Flexible couplings, such as jaw or grid couplings, can absorb radial misalignment by permitting some lateral deflection while transmitting torque.
It is essential to note that while shaft couplings can compensate for misalignments to some extent, they do have their limits. The magnitude of misalignment they can handle depends on the type and design of the coupling. Exceeding the specified misalignment capabilities of a coupling can lead to premature wear, reduced efficiency, and possible coupling failure.
Therefore, when selecting a shaft coupling for an application, it is crucial to consider the expected misalignment and choose a coupling that can accommodate the anticipated misalignment range. Additionally, maintaining proper alignment through regular maintenance and periodic inspections is essential to ensure the coupling’s optimal performance and extend its service life.
“`
How to Identify Signs of Wear or Failure in a Shaft Coupling
Regular inspection and monitoring are essential to identify signs of wear or potential failure in a shaft coupling. Detecting issues early can help prevent costly downtime and equipment damage. Here are common signs to look for:
1. Visible Damage:
Inspect the coupling for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, chips, or deformation. These can indicate mechanical stress or overload.
2. Abnormal Noise or Vibration:
Unusual noise or excessive vibration during operation may indicate misalignment, worn-out components, or a coupling nearing its failure point.
3. Increased Temperature:
If the coupling becomes noticeably hotter during operation than usual, it could be a sign of friction or misalignment issues.
4. Shaft Misalignment:
Check for misalignment between the shafts connected by the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and its components.
5. Excessive Backlash:
If the coupling exhibits too much free play or rotational play before torque transmission, it might indicate wear or fatigue in the coupling’s components.
6. Lubrication Issues:
Inspect the coupling for lubrication leaks or insufficient lubrication, which can lead to increased friction and wear.
7. Elastomeric Element Deterioration:
If the coupling uses elastomeric elements (e.g., rubber or polyurethane), check for signs of deterioration, such as cracking, softening, or deformation.
8. Bolts and Fasteners:
Examine the bolts and fasteners connecting the coupling components. Loose or damaged bolts can lead to misalignment and coupling failure.
9. Age and Service Life:
Consider the age and service life of the coupling. If it has been in use for a long time or exceeds the manufacturer’s recommended service life, it may be more susceptible to wear and failure.
10. Abnormal Performance:
Monitor the overall performance of the connected equipment. Any abnormal behavior, such as reduced power transmission or erratic operation, could be indicative of coupling issues.
If any of these signs are observed, it’s crucial to take immediate action. Depending on the severity of the issue, this may involve replacing worn components, realigning the shafts, or replacing the entire coupling. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections are key to identifying these signs early and ensuring the coupling operates optimally and safely.
“`
Best Practices for Installing a Shaft Coupling for Optimal Performance
Proper installation of a shaft coupling is crucial for ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature wear or failure. Follow these best practices to install a shaft coupling correctly:
1. Shaft Alignment:
Ensure that both the driving and driven shafts are properly aligned before installing the coupling. Misalignment can lead to increased stress on the coupling and other connected components, reducing efficiency and causing premature wear. Use alignment tools, such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems, to achieve accurate shaft alignment.
2. Cleanliness:
Before installation, clean the shaft ends and the coupling bore thoroughly. Remove any dirt, debris, or residue that could interfere with the coupling’s fit or cause misalignment.
3. Lubrication:
Apply the recommended lubricant to the coupling’s contact surfaces, such as the bore and shaft ends. Proper lubrication ensures smooth installation and reduces friction during operation.
4. Correct Fit:
Ensure that the coupling is the correct size and type for the application. Use couplings with the appropriate torque and speed ratings to match the equipment’s requirements.
5. Fastening:
Use the recommended fastening methods, such as set screws or keyways, to securely attach the coupling to the shafts. Make sure the fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specifications to prevent loosening during operation.
6. Spacer or Adapter:
If required, use a spacer or adapter to properly position the coupling on the shafts and maintain the desired distance between the driving and driven components.
7. Avoid Shaft Damage:
Be careful during installation to avoid damaging the shaft ends, especially when using set screws or other fastening methods. Shaft damage can lead to stress concentrations and eventual failure.
8. Check Runout:
After installation, check the coupling’s runout using a dial indicator to ensure that it rotates smoothly and without wobbling. Excessive runout can indicate misalignment or improper fit.
9. Periodic Inspection:
Regularly inspect the coupling and its components for signs of wear, misalignment, or damage. Perform routine maintenance as recommended by the manufacturer to prevent issues from worsening over time.
10. Follow Manufacturer’s Guidelines:
Always follow the manufacturer’s installation instructions and guidelines. Different types of couplings may have specific installation requirements that need to be adhered to for optimal performance and safety.
By following these best practices, you can ensure that your shaft coupling is installed correctly, maximizing its efficiency and reliability in your mechanical power transmission system.
“`

editor by CX 2024-04-19
Leave a Reply